A COMPLETE SELF EXAMINATION OF THE TESTICLES
These are clinical activities done to denote abnormalities of the testicles through palpation or observing any change in size and the shape of the testicles
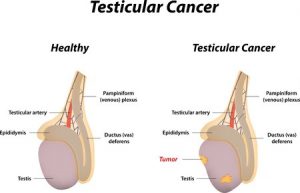
- Before embarking on the self examination of the testicles, we must look at the anatomy of the testicles so that we can distinguish between the normal and the abnormal.
TESTICLE ANATOMY
They include
- Testicles-they’s small oval-shaped glands, they produce the male gametes
- Epididymis-this are small tubes attached to the testicles, functions as the storage of sperms
- They also connect to the larger tubes called the vas-deferens
Scrotum -it’s a skin sac that a house the testicle, the sac plays a crucial role in spermatogenesis.
TESTICLES EXAMINATION
Expectations are;
- The testicles should be oval-shaped feel smooth and firm in the process of palpation. It’s done gently to note any change
- One testicle is expected to be larger than the other one
- Adult’s testicles range from about 15ml to 35ml in size
- One testicle should hang lower than the other one
There should be no pain or discomfort when the testicles and the scrotum are palpated gently with between the hands.
STEPS IN PERFORMING SELF EXAMINATION OF THE TESTICLES
It suitable to do the examination after a warm bath or shower and in front of the mirror so that you can be able to see your testis as you examine as well as feel
Cup one testis using both hands and test by rolling the testis in the scrotum between the fingers, press them lightly to avoid inflicting pain or causing injury yourself
During palpation make sure that you feel the presence of the spermatic cord and the epididymis tubes which are the structures that connect to each testis
You palpate look for the lumps in its texture, irregularities in the shape and its size and also note if there is any pain, always keep in mind that one testis is larger than the other one
Repeat the procedure to the other testis and also note the abnormal signs
During the process, if you observe any abnormality in the testis, such as pain, lumps, or fluid in the scrotum, it is advisable to seek medical attention from the physician.
After the self-diagnosis from the clinical features collected during the examination which may include
- Lumps and swelling
- Changes in the size of the testicles which may sometimes denote the early stage of elephantitis of the testis
- Irregular shape
- Purplish color scrotum which signals the incoming prostate cancer
NON-CANCEROUS CONDITIONS
Haematocele- it is a blood clothing caused to be the stressful conditions and the injury of the scrotum
Epididymis orchitis-it is the abnormality caused by information and pain in the testicles, and it can be managed antibiotics
Cyst-this are the fluid deposition in the testicles
Testicular torsion- is caused by the rapture of the cord connecting the testicles to the body
It requires urgent medical intervention.
Undescended testicles– this where testicles are missing from the scrotum either one or both